Investing can be confusing and complicated, even for the most seasoned investors.
There are many terms and concepts commonly used in finance that may not have an intuitive meaning to someone who is new to investing.
For this reason, we have compiled a glossary of terms that anyone looking to make investments should know about.
Jump to section: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
B
What is a Bear Market?
A bear market refers to a period when stock prices are generally falling with further falls anticipated.
What is a Black Swan?
A black swan is a rare and unpredictable event with big consequences. A ‘black swan event’ was popularised by Nicholas Taleb, who said black swans are rare enough to make even their contemplation difficult; have a catastrophic impact; and are often explained in hindsight as if they were predictable all along.
What is a Bull Market?
A bull market refers to a time when stock prices are generally rising, and participants expect price increases to continue.
C
What is a Capital Gain?
A capital gain refers to the difference between what you originally paid for an asset (including purchase costs like brokerage fees) and what you received when you sold the asset (less selling costs).
What is Cash Flow?
Cash flow is the net amount of cash and cash equivalents coming in and going out of a business. Cash received by a business represents cash inflows. Cash spent represents cash outflows.
Importantly, a company’s ability to create shareholder value rests on its ability to generate positive cash flows.
What is the difference between Cash Flow and Profit?
The difference between cash flow and profit is that while a firm’s profit shows the amount of money left after all expenses have been paid, cash flow indicates the net flow of cash coming in and out of the firm.
What is Compounding?
Compounding is the process of earning interest not only on your initial investment but also on any gains your investment earns. This means that an investor’s money can grow faster over time if they invest a certain amount and keep reinvesting their earnings.
In other words, compounding refers to the process where an asset’s earnings — either from capital gains or accrued interest — are reinvested to accumulate more earnings over time.
Compounding is not linear and can be conceptualised as interest on top of interest. Compounding was referred to by Warren Buffett as the eighth wonder of the world.
D
What is a Derivative?
A derivative is a security whose value depends on or is contingent on the values of other assets such as commodity prices, bond and stock prices, or market-index values.
Common examples of derivatives include futures contracts, options contracts, and credit default swaps.
What is a Dividend?
A dividend is a payment to shareholders from the company’s earnings.
Dividends are payments distributed to shareholders from company profits, usually made twice a year.
A dividend is a share of a company’s profits and depends on the number of shares an investor holds in the company. The size of the dividend will depend on how the company performs — sometimes a company may choose to withhold dividends to preserve cash. Not all companies pay dividends.
What is Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)?
Dollar-cost averaging is when an investor purchases a fixed number of shares on a regular schedule — for example, every six months.
With dollar-cost averaging, purchases are made regardless of the asset’s price. This strategy can smooth out price volatility by averaging out highs and lows over time, while also obviating the need to time the market.
E
What is Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortisation (EBITDA)?
EBITDA is the measure of a company’s profit before it has to pay interest or taxes.
It is a measure of the company’s overall financial performance, sometimes used as an alternative to net income.
Essentially, EBITDA measures a company’s profitability by excluding expenses related to debt by adding back interest and taxes to the company’s earnings.
Some analysts use EBITDA to evaluate and compare companies and industries and EBITDA eliminates the effects of financing and capital expenditures.
What are Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
Earnings per share is a ratio that reflects the amount of annual earnings available to shareholders, as stated on a per-share basis.
For instance, take a company with a reported net profit of $1.25 million who pays $250,000 in dividends and has 500,000 ordinary shares outstanding.
This firm would have an EPS ratio of $2. We get $2 by subtracting 250,000 from 1,250,000 and dividing the total by 500,000.
What is Equity?
Equity is another word for ownership stake.
An investor who owns stocks has ‘equity’ in that company — which means they may have some entitlements like voting rights in proportion to the number of shares — or equity — held in the company.
What is an Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)?
ETFs usually seek to mimic the performance of a specific index and can be quoted and traded on a stock exchange. ETFs allow investors to diversify with a single investment and gain broad exposure to the market.
ETFs can track indices like the S&P/ASX 200 Index but can also track the performance of a currency or commodity.
F
What is Financing?
Financing refers to the process of acquiring funds to fund one’s business activities, purchases, or investments. Financial institutions like banks are the predominant source of financing.
Financing is important in granting businesses capital they can put to productive use that may have — without financing — been out of immediate reach. Of course, financing creates debt.
What is Financial Ratios Analysis?
Financial ratios are used by financial analysts to compare aspects of one company with another — for example, comparing profitability between two companies’ divisions. Financial ratios can also be used to track a stock’s performance over time, for instance, if you want to know what your return on equity was last year compared with this year.
Some common financial ratios are price-earnings, earnings per share, debt-to-equity, and return on equity.
What is Fundamental Analysis?
Fundamental analysis is a style of investing that relies on economic and company-specific data to determine the stock’s fair value.
Fundamental analysis involves researching determinants of a stock’s value, including earnings and dividends prospects, expectations of future returns, and competitive risk.
What are Futures?
A futures contract is a financial instrument that obliges market participants to purchase or sell a financial asset at an agreed upon price at a specified future date.
G
What is Goodwill and Intangible Assets?
Tangible fixed assets are items like buildings, equipment, or vehicles. But when a company is bought for a premium over its book value — which incorporates these tangible assets — the difference is labelled goodwill and listed on the balance sheet as an intangible fixed asset.
Goodwill can refer to things like patents, trademarks, domain names, copyrights, and trade secrets that provide additional income without being physically tangible in nature.
What is Gross Profit Margin?
Gross profit margin is a financial metric assessing a company’s financial health by calculating the amount a firm has left over from its sales after subtracting the cost of those sales.
Gross profit margin helps assess the extent to which an organisation can cover its costs through sales alone.
H
What is a High-Yield Investment?
High-yield investments are securities which offer higher rates of potential return but also require taking on more risk. You could lose some or all of your money on high-risk investments.
I
What is an Initial Public Offering (IPO)?
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the first instance of a company’s stock being sold to the public. In other words, an initial public offering is the first issue of shares to the general public by a previously private firm.
L
What is Liquidity?
Liquidity refers to the speed and ease with which an asset or security can be bought or sold in the market. In more technical terms, liquidity is the ease of realising the cash value of one’s investment.
liquid assets like real estate, for instance, can be harder and slower to sell than a stock that trades millions of shares daily.
M
What is a Managed Fund?
Managed funds pool together investors’ money and then buy and sell assets on investors’ behalf.
Managed fund investors don’t own the underlying investments. Instead, they own ‘units’ in the fund. The value of these units will fluctuate with the value of the underlying assets. Some managed funds also pay income or distributions.
What is Market Capitalisation?
Market capitalisation is the total value of all outstanding shares. Market capitalisation is calculated by multiplying a company’s current share price by the total number of outstanding shares.
Market cap can be used to categorise stocks into small-caps, mid-caps, and large-caps.
Large-caps are companies with the largest market capitalisation, frequently associated with the S&P/ASX 50. Small-caps are stocks that sit outside the largest 100 stocks on the ASX by market cap and are usually higher risk investments.
What are Mutual Funds?
A mutual fund is an American term describing a managed investment. Like managed investments, mutual funds pool investors’ money and invest it into stocks, bonds, or other securities.
The mutual fund then pays dividends to shareholders based on their holdings — but they also charge fees for managing investments, so not all returns go back into investor pockets.
N
What is Net Asset Value (NAV)?
Net asset value is the book value of a company’s assets divided by the number of shares on issue. Specifically, NAV represents the value of assets less liabilities, expressed as a per-unit or per-share value.
Net asset value is frequently used to measure the rate of return on an investment in a managed (mutual) fund.
O
What are Options?
An options contract between two parties gives the taker (buyer) the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a particular price on or before a particular date.
For instance, a September call option on CBA stock with an exercise price of $90 entitles the option’s owner to purchase CBA shares for $90 at any time up to, and including, the expiration date in September.
P
What is a Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio?
A price-to-earnings ratio (P/E) is a financial ratio that takes the current price of a share and divides it by the earnings per share. PE ratios can be used to assess whether a particular stock’s share price is over- or undervalued to its peers.
A P/E ratio expresses how much investors must pay per dollar of earnings a stock generates for each share.
Q
What is Quantitative Easing (QE) and how does it work?
Quantitative easing is a tool used to stimulate the economy. Quantitative easing is also known as bond purchases, where central banks purchase bonds to provide extra stimulus to the economy.
QE is a monetary policy strategy aimed at lowering interest rates, increasing the supply of money, and encouraging more lending to consumers and businesses.
QE works by upping demand in the securities central banks buy on a mass scale. In turn, the rising demand in these securities lowers their yields (interest rates).
R
What is a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT)?
REITs are trusts that invest in a range of real estate — residential, commercial, or industrial. REITs expose investors to the value and rental income from properties owned by them. Investing in a REIT can be a less cost-intensive way to gain exposure to the property market.
What is Return on Investment (ROI)?
Return on investment (ROI) is a measure of the profitability of an investment relative to its cost. In other words, ROI is earnings from investments over a given period — generally expressed as a percentage per year of the amount invested.
S
What are Securities?
Securities are a broad category of investment assets. Securities can be categorised into equity securities (like stocks), debt securities (like bonds and debentures), and derivatives (like futures and options).
What is the Sharpe Ratio?
The Sharpe ratio measures the risk-adjusted return an investor achieves for each unit of volatility or systematic risk they take on. The Sharpe ratio is also known as the reward-to-volatility ratio.
Sharpe Ratio = (Asset Return – Risk-Free Rate) / Standard Deviation
What is a Shareholder?
Shareholders own an equity stake in a publicly traded company via purchasing the company’s shares. Shareholders usually possess some voting rights and are entitled to dividends — which represent shareholders’ portion of a firm’s profits.
What is Short Selling?
Short selling refers to selling a security you do not yet own. Under short selling, you borrow the security from a third party (a broker) and immediately sell it to a buyer. You then try to buy identical securities at a later date for a lower price to return them to your lender.
Shorting is a speculative investment made when you believe the price of a security will fall and you can make a profit in pocketing the difference between your sale price and your purchase price at a later date. However, short selling is a riskier investment because if prices rise, your potential loss can be more than the value of your investment.
What are Stocks?
Stocks represent partial ownership of a company. Stocks are also known as equities or shares. Stock owners — or shareholders — are entitled to certain voting rights as well as any dividends from the company’s profits.
What is a Stop-Loss Order?
A stop-loss order is an instruction to sell a security if it falls below a threshold price you set. Stop-loss orders minimise your losses. In other words, stop-loss orders are predetermined sell orders at a price below the current price intended to minimise losses in the event of further falls.
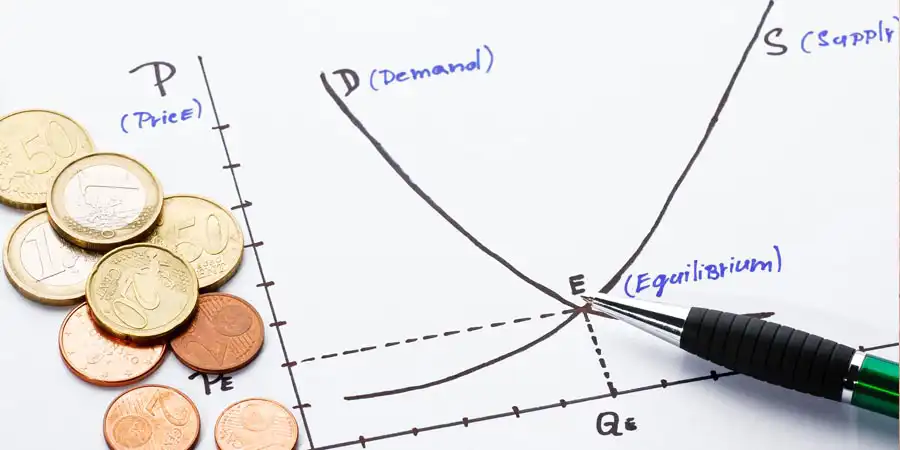
What is the Law of Supply and Demand?
The law of supply and demand is a fundamental principle in economics that states that the price of any particular good will increase if demand for it exceeds supply, as buyers compete for what they perceive to be an increasingly scarce resource.
T
What is Technical Analysis?
Technical analysis uses charts of trading patterns to identify trends and make predictions about future prices. Technical analysts — or chartists — study price charts to pick out trends in the hope of capitalising on emerging patterns.
What is the difference between Investing and Trading?
Investing involves buying shares with an expectation for long-term capital growth. Trading involves short-term strategies that focus on daily, monthly, or quarterly profit opportunities.
Investing may mean holding stocks for years, whereas trading involves much more frequent transactions to capitalise on short-term market fluctuations.
What are Treasury Bills?
A Treasury Bill (T-Bill) is a short-term US government debt security backed by the US Treasury Department. T-Bills usually have a maturity of one year or less. T-Bills, like Australian Commonwealth Government bonds, are considered to be lower-risk investments.
How does a Trust work?
A trust represents an obligation by a trustee to hold property for the benefit of the trust’s beneficiaries. There are many types of trusts, including cash management unit trusts, public unit trusts, discretionary unit trusts, fixed trusts, and deceased trusts.
U
What is a Unit Trust Fund?
A unit trust fund is an investment vehicle where investors purchase whole shares in a portfolio (rather than individual securities) on which they are entitled to dividends from all investments, provided there is enough profit retained by the manager after fees have been paid out.
What is an Underlying Asset?
Underlying assets can be anything from stocks, commodities like gold or oil, currencies, bonds — basically any financial asset upon which a derivative’s price is based. Derivatives are financial instruments whose price depends on a different asset. Basically, underlying assets give derivatives their value.
V
What is Value Investing?
Value investing — also regarded as fundamental analysis — involves thorough evaluation of corporate financial statements and qualitative business analysis to uncover value before the market catches on. Essentially, value investing seeks to pick out stocks that appear to be trading at a discount to their intrinsic or fair value.
What is VIX and why do people use it?
VIX (CBOE Volatility Index) is the ticker symbol for the futures contract on the 30-day implied volatility of the S&P 500 that trades on the CBOE Futures Exchange.
The VIX reflects the market’s expectations for the relative strength of near-term price changes of the major US index, the S&P 500. The VIX is an important measure used by market participants to gauge market sentiment, specifically the level of fear among investors.
What is Volatility?
Volatility is the extent to which returns on assets fluctuate over time. In finance, volatility is measured by the rate at which an asset’s price moves up and down.
Assets with little price fluctuation are deemed less volatile. Conversely, assets with frequent and large price movements are deemed more volatile.
What are Volatile Stocks?
Volatile stocks are stocks whose price fluctuates frequently and whose price can move up and down greatly. Volatile stocks present investors with great opportunities for gain but also expose them to a greater amount of risk of loss.
W
What are WAAAX Shares?
WAAAX shares are an acronym for ASX tech stocks WiseTech Global Ltd [ASX:WTC], Afterpay Ltd [ASX:APT], Appen Ltd [ASX:APX], Altium Ltd [ASX:ALU], and Xero Ltd [ASX:XRO].
WAAAX is Australia’s tech version of America’s FAANG stocks. FAANG is an acronym for Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, and Alphabet (Google).
What is a Warrant?
Warrants are financial products issued by a bank or another financial institution giving you the right to buy securities (shares, currencies, indices, or commodities) at a set price within a determined time, traded on the ASX.
Final Thoughts
If you’re looking to invest, it’s important to understand the concepts and terms used by investors and finance professionals. Hopefully, this glossary helped demystify some of these terms. If unsure about an investment, consult your financial adviser.